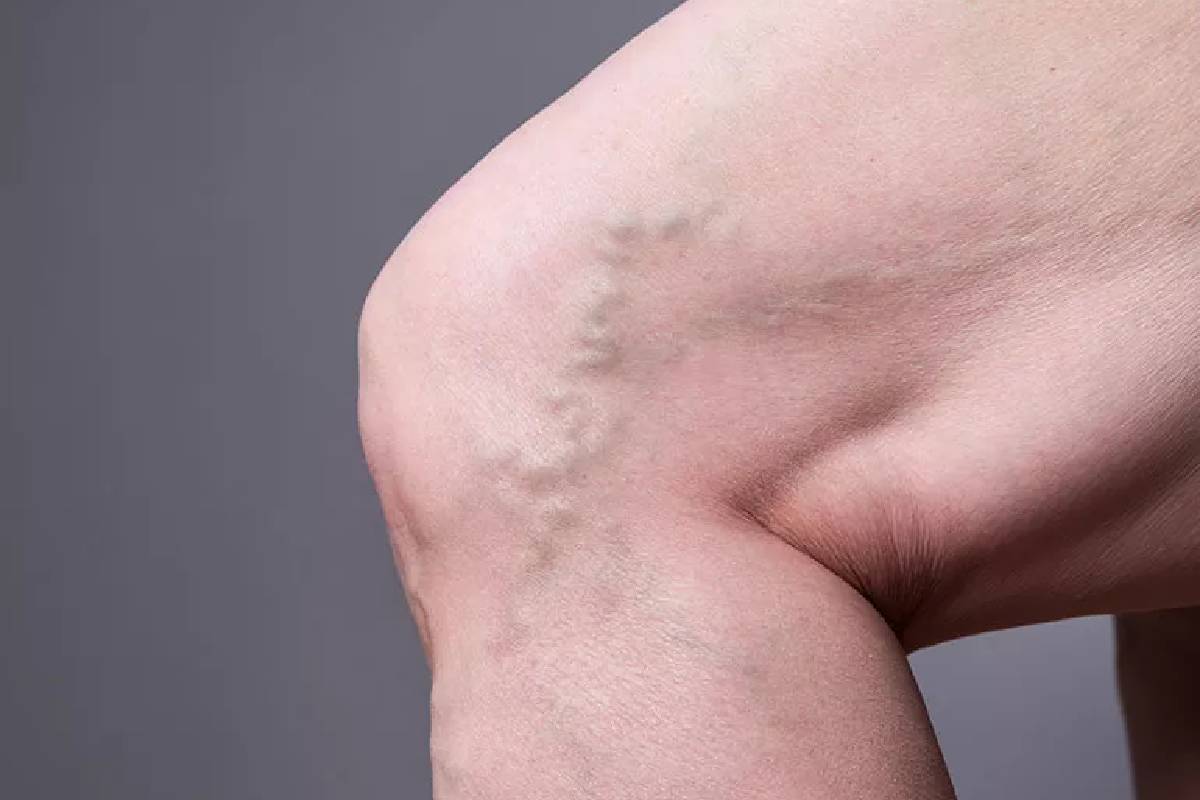
Varicose veins afflict millions globally, evolving from a trivial cosmetic worry into a broad health and functional dilemma that subtly constrains everyday activities. These obtrusive, enlarged surface veins do more than mar appearance—they indicate modifying circulatory dynamics that warrant investigation and timely intervention. Comprehending the genesis of varicose veins and weaving counter-strategies into daily practice can substantially enhance both current ease and enduring vascular integrity.
Mechanisms of Varicose Vein Formation
The human circulatory apparatus is supported by a sophisticated arrangement of unidirectional valves concentrated in the venous system, which husband blood flow back to the heart, opposing gravitational descent. When these valves sustain insufficiency or become structurally compromised, retrograde blood accumulation occurs, leading to venous distension, tortuosity, and striking surface prominence. The phenomenon chiefly localizes to the lower limbs, where hydrostatic pressure is maximal and the challenge of upward transport is persistent and pronounced.
Multiple interrelated mechanisms drive deterioration of venous valves and, ultimately, the formation of varicose veins. Heritable predisposition remains at the forefront; an affected lineage constitutes one of the most reliable prognostic markers. Temporary or sustained fluctuation in gonadal steroid levels—seen in pregnancy, the menopausal transition, and specific endocrine pharmaceuticals—compromises connective tissue strength and, accordingly, valve competency. Cumulative senescence of the venous wall, intricately designed to resist luminal hypertension, is further aggravated by statically applied hydrostatic loads during occupations that mandate prolonged standing or immobility.
Pathogenesis and Early Interventions
Insights into these pathogenic pathways clarify the slow and insidious natural history of varicose veins, underscoring that non-operative imposition of weight reduction, pneumatic compression, and periodic elevation of the lower limbs may defer or arrest valve rupture.
Functional Consequences of Varicose Veins
Consequences of varicosity extend beyond dermatological concern. Pathophysiological stagnation engendered by incompetent perforating and saphenous valves steadily raises venous hydrostatic pressure, triggering intrinsic neurite invasion and peri-vascular edema. Resultant symptoms—mid-calf or medial thigh heaviness, post-phlebitic paresthesias, and pronounced evening exertional hyperemia—progress in intensity during the orthostatic work shift, and abrade the individual’s adaptive and occupational performance. Effective countermeasures, addressing venous congestion, do not restore a commensurate anatomical rehabilitation; instead, they shift the management paradigm from aesthetics to the mitigation of daily and cumulative microvascular symptom load.
The Daily Burden of Symptoms
Many people report their legs feeling heavy and fatigued for a duration and intensity disproportionate to any measurable exertion. This profound tiredness often disrupts not only planned exercise but also household chores and social outings, with discomfort peaking by late afternoon or early evening. Complaints are routinely accompanied by swelling that settles in the lower extremities and, when varicose veins are present, skin tightness that makes even properly fitted shoes feel restrictive. Muscle cramps, especially nocturnal, compound the issue and frequently alter sleep architecture, leading to diminished daytime vigor.
Skin Changes and Chronic Progression
Advanced varicosities can further compromise skin integrity. Affected dermis may develop a mottled, browning hue, accompanied by xerosis and heightened reactivity. Patients often report pruritus or pseudo-burning pain that becomes a nearly continuous gremlin, impeding attentional focus and accelerating the avoidance of favorable lower-extremity activity. This avoidance, in turn, contributes to ever-worsening venous stasis and a lasting downward spiral, thereby underscoring the necessity of early, consistent intervention beyond cosmetic concern.
The Role of Physical Activity
Structured but moderate physical activity remains among the most efficacious countermeasures against worsening venous insufficiency. High-impact or prolonged duration exercise is neither practical nor advisable. Rather, walking, often underestimated, prompts rhythmic contraction of the calf musculature—nature’s venous pump. A 10-minute threshold, repeated two to four times over the day, suffices to generate clinically meaningful increases in venous return, rendering the intervention both practical to prescribe and comforting to perform for individuals of any baseline fitness level or daily itinerary.
Benefits of Aquatic Movement
Physical activity in aquatic settings confers substantial advantages for individuals managing varicose veins. The hydrostatic pressure exerted by water functions like a built-in compression garment, enhancing venous return without imposing the impact that terrestrial exercise frequently creates for veins already weakened. Furthermore, water’s buoyancy alleviates discomfort in the lower extremities, fostering a degree of mobility that is often unattainable on dry ground.
Mini-Exercises for Stationary Settings
Even brief, strategically executed exercises performed during stationary intervals can dramatically shift venous dynamics. Ankle dorsiflexion, calf muscle contractions, and lower-leg elevation performed in a seated position moderate the venous stasis that accompanies long periods of immobility. Employees confined to desks may cultivate lasting habits by scheduling discreet reminders for such mini-sessions or integrating 2–3 minute walking intermissions, thereby reinforcing sustained lower-limb perfusion.
Yoga, Stretching, and Relaxation
Complementary to structured exercise, the systematic inclusion of restorative yoga and carefully sequenced stretching routines, predominantly those that facilitate elevation or gentle inversion of the legs, may further refine peripheral hemodynamics. These regimens simultaneously lower systemic stress through relaxation, an effect that corticosteroid and cytokine modulation may amplify, thereby conferring an additive, if indirect, anti-inflammatory influence on the venous system and, by extension, on overall cardiovascular integrity.
Nutrition and Circulatory Health
Supporting vascular health requires a more nuanced approach than simply adhering to general dietary recommendations; a targeted intake of specific nutrients, paired with intentional eating patterns, is essential to maintain robust circulation and effective venous function. Antioxidant-rich foods serve a pivotal protective function, shielding endothelial cells from oxidative damage and inflammation, both of which are implicated in the structural weakening of venous walls. Berries, dark leafy greens, and a broad spectrum of brightly colored vegetables offer concentrated phytochemicals that reinforce vascular integrity.
Flavonoids and Vascular Strength
Flavonoids are particularly advantageous for the venous system and are most prevalent in citrus fruits, various grape cultivars, and high-cocoa dark chocolate. Clinical and epidemiological studies indicate that these compounds improve endothelial function, enhance venous tone, and reduce venous distensibility, thereby providing prophylactic aid against the prominence of varicose veins. Including a diverse array of flavonoid-rich foods within daily meals supplies a steady reservoir of protective phytochemicals supportive of venous health.
Hydration, Sodium, and Fiber Balance
Hydration directly modulates blood viscosity, facilitating unobstructed microcirculation, while excessive sodium can precipitate fluid retention, thereby increasing hydrostatic pressure within veins. Cultivating a dietary approach that equilibrates these two factors, alongside regulating overall sodium intake, establishes a hemodynamically stable environment. Further, foods high in dietary fiber mitigate constipation, diminishing elevated intra-abdominal pressure that can exacerbate venous distension in susceptible individuals.
Weight Management and Vein Health
Sustaining an appropriate body weight alleviates persistent mechanical pressure on the lower limb venous system and is integral to broader cardiovascular well-being. Rather than adopting severe caloric restrictions, the prioritization of foods rich in essential nutrients and the cultivation of moderate, enduring eating behaviors confer enduring advantages to both venous integrity and general health.
The Importance of Professional Care
Although behavioral adjustments remain the first line of defence in both the prevention and conservative management of varicose veins, knowing when to obtain expert assessment maximises therapeutic benefit. Timely referral to physicians specialized in vascular medicine may detect latent venous insufficiency before complications develop, thus forestalling disease progression and retaining functional capacity. Contemporary interventions have become less invasive, featuring techniques that correct varicosities through small incisions and allow immediate reinstatement of routine daily movement. Consequently, professionally directed care is not a substitute for healthy living but a supplement that consolidates lifestyle interventions into a cohesive, unified management protocol.
For residents of Central Florida in search of expert attention, the Vein Clinics in Winter Haven offer both cutting-edge diagnostic methodologies and targeted therapeutic modalities. A formal examination will ascertain the optimum therapeutic course, informed by the patient’s clinical status, symptom burden, and individual health aspirations.
Long-Term Care and Follow-Up
Routine follow-up and clinical evaluation guarantee that both non-invasive and interventional therapies yield sustained, maximal efficacy throughout the disease trajectory. Such continual engagement with health professionals allows for the recalibration of treatment strategies in response to changing clinical presentations and the advent of novel therapeutic modalities.
Cultivating Lasting Preventive Practices
Durable control of varicose veins is achieved not through intermittent, sweeping lifestyle rewrites, but by forging manageable, incremental behaviours that fit naturally within the everyday pattern. Modest, sustained adjustments typically confer greater benefit, and greater longevity, than ambitious, scripted regimens that see compliance erode over time.
Structuring the Environment for Health
Intentional structuring of the environment to favour health serves to institutionalise these behaviours. Examples include designating a comfortable zone for elevating the legs, retaining well-fitting walking footwear near the front door to prompt brief ambulations, and assembling nutritious, readily available snacks that bolster vascular integrity. Such foresight diminishes friction at the point of choice, favouring action over inertia.
Vigilance and Self-Education
Self-education about intrinsic risks and the earliest manifestations of vascular distress allows for vigilant, anticipatory stewardship. Routine, systematic self-examination, along with surveillance of leg comfort, external morphology, or functional ability, ensures that subtler changes trigger prompt, focused, and protective therapeutic measures, thereby maintaining both physiological well-being and the capacity for desired daily activities.
Integrating Vein Health Into Holistic Wellness
Embedding varicose-vein prevention within comprehensive wellness regimens solidifies the interdependence of vascular integrity and holistic health, thereby furnishing a compelling rationale for the habitual adoption of lifestyle interventions that further distal health objectives.